
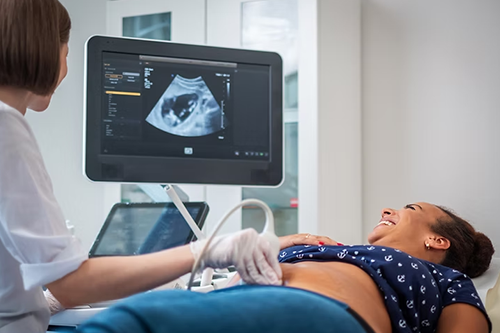
"Sonography" is another term for ultrasound imaging — a medical diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It’s commonly used to visualize:
X-rays pass through the body and are captured by a digital detector.
Dense structures like bones appear white, while softer tissues appear in shades of gray or black.
The image is converted into a digital file and displayed on a computer screen.
Faster results – Images are available instantly.
Lower radiation exposure - than traditional film X-rays.
Enhanced image quality – Zoom in, adjust contrast, or apply filters.
Easier storage & sharing – Files can be stored in electronic health records (EHR) or shared with specialists.
Environmentally friendly – No need for film or chemicals.
Computed Radiography (CR) : Uses a cassette-based system with digital sensors.
Direct Digital Radiography (DR) : Uses flat panel detectors and provides real-time imaging.
Want a comparison between digital and traditional X-rays? Or are you looking for something specific, like cost, risks, or how to prepare for one?

 For sonography and Xrays
For sonography and Xrays
 (For CT scan and MRI)
(For CT scan and MRI)